Enterprise software no longer competes on features alone. It competes on how fast decisions are made, how accurately performance is measured, and how quickly leaders can respond to change. That is exactly why enterprise BI has moved from a “nice-to-have” analytics layer to a core operating system for decision-making.
Today, every serious enterprise application — whether it is ERP, CRM, HRMS, FSM, construction management, or financial systems — must embed or integrate BI at its core.
However, not all analytics are created equal.
True enterprise BI is not about pretty dashboards. Instead, it is about governance, scale, trust, performance, security, and decision velocity. Therefore, choosing the right BI features is a strategic architecture decision, not a UI decision.
In this definitive guide, you will learn:
- What enterprise BI really means in modern enterprises
- Why basic reporting tools fail at scale
- The must-have BI features for any serious enterprise application
- How BI drives adoption, ROI, and competitive advantage
- How to evaluate an BI platform properly
Let us begin with the fundamentals.
What Is Enterprise BI?
It (Enterprise Business Intelligence) is a scalable, governed, secure, and performance-driven analytics layer that supports decision-making across the entire organization—from frontline teams to executive leadership.
Unlike basic BI tools, enterprise BI:
- Serves hundreds or thousands of users
- Handles millions or billions of rows of data
- Enforces data governance and security
- Supports mission-critical business workflows
- Integrates deeply into core enterprise applications
In other words, BI is not a reporting tool. It is a decision infrastructure.
Why Basic BI Fails in Enterprise Environments
Many organizations start with simple dashboards. However, they quickly hit limitations.
Basic BI fails because:
- It cannot scale to large data volumes
- It breaks under concurrent user load
- It lacks role-based security and governance
- It creates multiple versions of truth
- It depends heavily on analysts instead of business users
- It does not integrate deeply into enterprise workflows
As a result, enterprises either:
- Lose trust in data
- Slow down decision-making
- Or build expensive, fragmented analytics stacks
This is exactly why enterprise BI exists.
The Strategic Role of Enterprise BI in Enterprise Applications
Modern enterprise applications are no longer transactional systems only. They are decision platforms.
Therefore, BI must:
- Power daily operational decisions
- Support strategic leadership decisions
- Enable cross-department visibility
- Drive process optimization
- Enforce data accountability
- Accelerate business execution
Consequently, BI becomes a core competitive advantage.
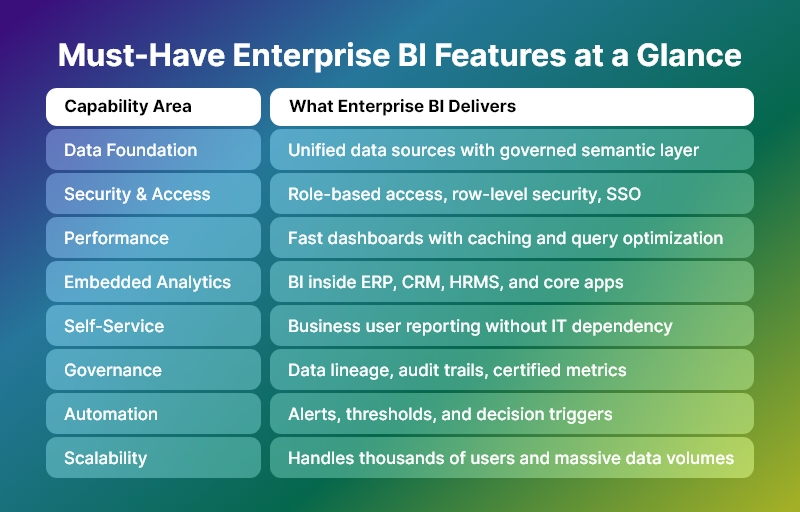
Must-Have Enterprise BI Features (Complete Enterprise Checklist)
Below is the definitive feature framework for evaluating or building a true BI system.
1. Enterprise-Grade Data Architecture
BI must handle complexity at scale.
It must support:
- Multiple data sources (ERP, CRM, HRMS, IoT, Finance, Ops, external data)
- Structured and semi-structured data
- Large volumes and high refresh rates
- Historical and real-time data together
Core capabilities include:
- Data connectors and ingestion pipelines
- Data modeling and semantic layers
- Incremental refresh and caching
- Support for cloud, on-prem, and hybrid data
Without this foundation, enterprise BI collapses under growth.
2. Single Source of Truth (Semantic Layer)
One of the biggest reasons BI fails is metric chaos.
Therefore, enterprise BI must provide:
- Centralized metric definitions
- Business-friendly semantic models
- Reusable KPIs across dashboards and apps
- Governance over calculations and logic
Benefits:
- No conflicting numbers
- No department-level data politics
- No spreadsheet shadow systems
- High trust in executive reporting
In short, BI must enforce truth at scale.
3. Enterprise Security and Access Control
Enterprise BI is useless if it is not secure.
It must support:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Row-level and column-level security
- SSO and enterprise authentication (SAML, OAuth, LDAP, etc.)
- Audit logs and access tracking
- Data masking for sensitive fields
Why this matters:
- Finance, HR, and leadership data must not leak
- Compliance requirements demand strict controls
- Large organizations cannot rely on manual permissions
Therefore, security is not optional in BI. It is foundational.
4. Performance at Scale
Enterprise BI must stay fast even when:
- Data grows 10x
- Users grow 50x
- Queries become complex
- Dashboards become heavier
Critical performance features include:
- Intelligent caching
- Query optimization
- In-memory acceleration
- Pre-aggregations
- Load balancing
- Asynchronous query execution
Because in enterprises:
If dashboards are slow, decisions are slow. And slow decisions cost money.
5. Embedded Analytics for Enterprise Applications
Modern enterprise BI must not live in a separate portal.
Instead, it must:
- Embed inside ERP, CRM, HRMS, FSM, or industry apps
- Respect application user permissions
- Adapt to application workflows
- Feel like a native feature
Embedded BI enables:
- Contextual decision-making
- Higher adoption
- Better user experience
- Stronger product differentiation
Today, enterprise BI is a product feature, not a separate product.
6. Self-Service Analytics for Business Users
BI cannot depend entirely on analysts.
It must empower:
- Managers
- Operations leaders
- Finance teams
- Sales leaders
- Department heads
Self-service features include:
- Drag-and-drop reports
- Filter and slice-and-dice
- Drill-down and drill-through
- Custom views and saved dashboards
- Ad-hoc exploration without SQL
This ensures:
- Faster answers
- Less dependency on data teams
- Higher data culture maturity
7. Advanced Dashboarding and Visualization
Enterprise BI dashboards must support:
- Executive-level KPI views
- Operational performance views
- Departmental scorecards
- Process monitoring screens
Core visualization capabilities:
- Interactive charts and tables
- Cross-filtering
- Drill-down hierarchies
- Conditional formatting
- Alerts and thresholds
- Storytelling views
However, remember:
Enterprise BI is not about visuals. It is about decisions enabled by visuals.
8. Real-Time and Near Real-Time Analytics
Many enterprise use cases require:
- Live operations monitoring
- SLA tracking
- Incident detection
- Financial risk control
- Supply chain visibility
Therefore, BI should support:
- Streaming or near-real-time data
- Incremental refresh
- Low-latency dashboards
- Operational alerting
This transforms enterprise BI from reporting to control systems.
9. Alerts, Automation, and Decision Triggers
Modern BI must not wait for users to open dashboards.
It must:
- Push alerts when thresholds are crossed
- Trigger workflows
- Send notifications to email, Slack, Teams, etc.
- Integrate with business processes
Examples:
- Alert when cash flow drops below limit
- Alert when project cost overruns
- Alert when churn risk spikes
- When compliance metrics fail
This is how enterprise BI becomes proactive instead of reactive.
10. Data Governance and Lineage
At enterprise scale, governance is non-negotiable.
- BI must provide:
- Data lineage tracking
- Impact analysis
- Change management
- Certification of datasets
- Ownership and stewardship models
This ensures:
- Audit readiness
- Compliance confidence
- Trust in enterprise-wide metrics
- Controlled evolution of analytics
11. Collaboration and Sharing
Enterprise BI is a team sport.
It must support:
- Shared dashboards
- Commenting and annotations
- Versioning
- Scheduled reports
- Role-based sharing
This transforms analytics into organizational conversation, not isolated analysis.
12. AI and Advanced Analytics (Optional but Strategic)
Modern enterprise BI increasingly includes:
- Forecasting
- Anomaly detection
- Trend analysis
- What-if simulations
- Natural language queries
While not mandatory for every enterprise today, this is rapidly becoming a strategic differentiator.
13. Scalability and Future-Proof Architecture
Enterprise BI must scale across:
- Users
- Data volume
- Use cases
- Departments
- Geographies
Therefore, it must support:
- Modular architecture
- API-first integration
- Cloud and hybrid deployment
- Horizontal scaling
- Multi-tenant or multi-org setups
How Enterprise BI Drives Real Business Outcomes
When implemented correctly, BI delivers:
- Faster decision cycles
- Higher operational efficiency
- Lower reporting overhead
- Better leadership visibility
- Stronger governance
- Higher ROI from enterprise systems
In short:
BI turns data into organizational leverage.
How to Evaluate an Enterprise BI Platform
Use this checklist:
- Does it scale to thousands of users?
- Does it enforce governance and security?
- Does it embed inside your application?
- Does it support self-service safely?
- Does it perform under heavy load?
- Does it integrate with your data stack?
- Does it reduce dependency on analysts?
If the answer is “no” to several of these, it is not true BI.
Final Thoughts: Enterprise BI Is Not Optional Anymore
In 2026 and beyond, BI is not an add-on.
It is:
- A core layer of enterprise architecture
- A strategic decision platform
- A competitive advantage
- A governance system
- A performance engine
Organizations that treat BI as a strategic system will out-execute, out-learn, and out-scale those that do not.
And that is the real power of BI.

