What Does “Testing” Means ?
Testing of a product of services is an investigation to find out how well it is working against the expectation. Thus the quality of product can be assessed. Whether computer hardware or software development, testing is done at key checkpoints in the overall process to determine whether objectives are being met.
What is TDD (Test-Driven Development) ?
TDD is a way of designing the code by writing a test which expresses what you intend the code to do. It defines a set of rules for developing software in which test cases are written before any code and the only code written will be enough to make the tests pass.
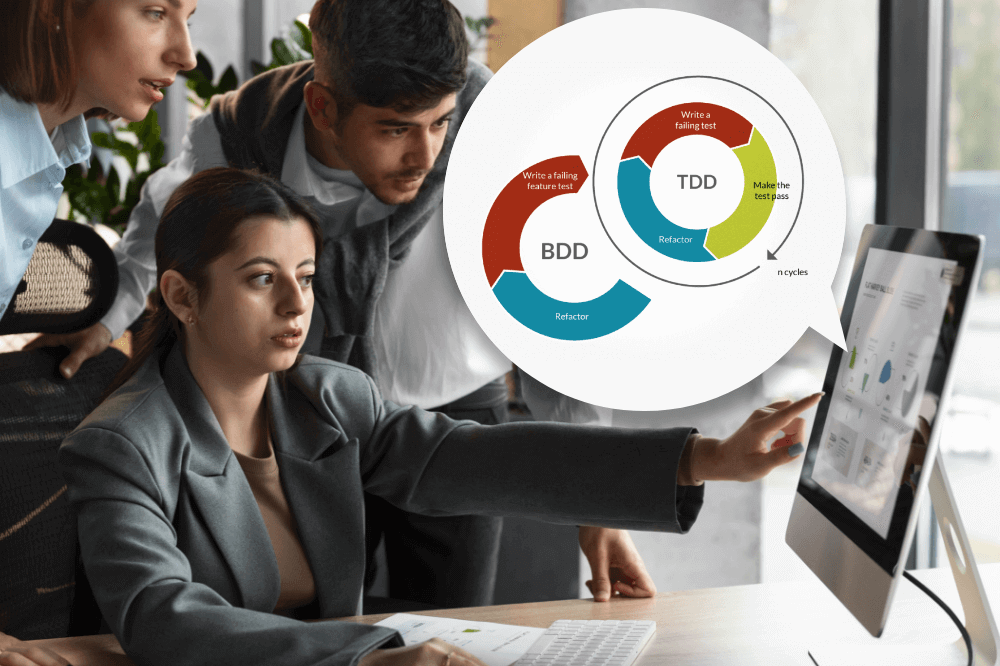
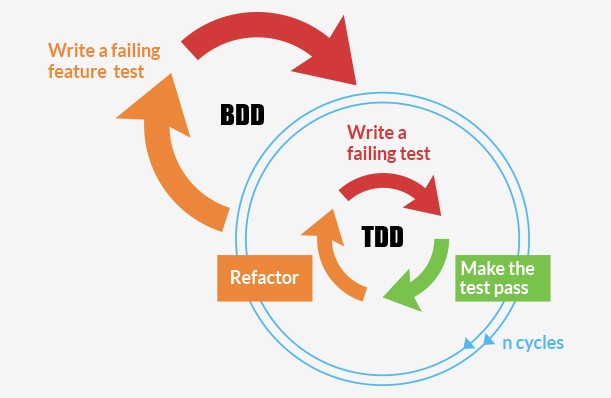
TDD is basically a software development technique that relies on the repetition of a very short development cycle. In this technique, first the developer starts by writing a failing automated test case (Red), implement the simplest solution that will pass the test cases (Green) and then finally improves or refactor the code (Refactor).”RED-GREEN-REFACTOR” is the main agenda for TDD.
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development process that focuses on writing tests before writing the actual code. The TDD cycle typically follows three steps:
- Write a Test:
Developers begin by writing a test that defines the desired behavior of a particular piece of code. This test initially fails because the code to fulfill the behavior hasn’t been implemented yet. - Write Code:
Next, the developer writes the minimum amount of code necessary to make the test pass. This phase emphasizes simplicity and getting the code to work. - Refactor:
After the test passes, developers refactor the code to improve its quality, maintainability, and efficiency. This step ensures that the codebase remains clean and easy to maintain.
TDD is renowned for its ability to catch bugs early in the development process, enhance code quality, and provide clear documentation of how the code is intended to work.
Tools to use:
There are some popular gems available to implement TDD in Ruby on Rails like rspec-rails, capybara, factory_girl_rails, spork, launchy etc…
Example:
Below is the code snippet for writing controller tests, like this:
[sourcecode language=”plain”]
describe ArticlesController do
it "renders the index template" do
get :index
response.should render_template("index")
end
end[/sourcecode]
What is BDD (Behavior-Driven Development)?
BDD extends Test driven development by writing test cases in a way anyone can understand.With the help of BDD, software development is managed by both business interests and technical insight.
It focuses and associates behavioral specifications with each unit of software under development.
Basically BDD is an Agile software development technique that encourages collaboration between developers, QA and non-technical or business participants in a software project.
It extends TDD by writing test cases in a natural language that non-programmers can read. In other way it is like story writing.
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) is an extension of TDD that focuses on the behavior of software from the user’s perspective.
BDD emphasizes collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to ensure that the software meets the desired behaviors and outcomes. Key components of BDD include:
- Specifying Behavior:
In BDD, behaviors are specified using human-readable language, often in the form of “Given-When-Then” scenarios. These scenarios describe the expected behavior of the software from the user’s viewpoint. - Collaboration:
BDD promotes collaboration between technical and non-technical team members. Developers, testers, and business stakeholders work together to define and understand the software’s behavior.
Automated Testing: BDD scenarios are translated into automated tests that verify the desired behaviors. These tests serve as living documentation that ensures the software aligns with the intended behavior.
The main thing to know is that BDD is meant to eliminate issues that TDD might cause.
Tools to use:
Some popular gems are available to implement BDD in Rails are rpsec-rails, factory_girl_rails, cucumber-rails, guard-cucumber, mocha etc…
Example:
Below is the code snippet for writing the BDD:
[sourcecode language=”plain”]
#articles.feature
Given an article exists called "Testing Demonstration"
When I visit the list of articles
Then I should see an article called "Testing Demonstration"
#article_steps.rb
Given /^an article exists called "(.+)"$/ do |title|
FactoryGirl.create(:article, title: title)
end
When /^I visit the list of articles$/ do
visit articles_path
end
Then /^I should see an article called "(.+)"$/ do |title|
page.should have_content title
end
[/sourcecode]
TDD or BDD, which is better?
The main difference between TDD and BDD is the business readability factor. BDD’s main draw is that the specifications or features are separate from the test code, so the product owners can provide or review the specification without having to go through code.
TDD has a similar mechanism, but instead you describe a step with a Describe, Context or It block that contains the business specification, and then immediately have the code that executes that statement.
Few drawbacks of TDD are as follows:
- Big time investment: For the simple case you lose about 20% of the actual implementation, but for complicated cases you lose much more.
- Additional Complexity: For complex cases, test cases are harder to calculate.
- Design Impacts: Sometimes the design is not clear at the start and evolves as you go along – this will force you to redo your test which will generate a big time lose.
- Continuous Tweaking: For data structures and black box algorithms unit tests would be perfect, but for algorithms that tend to change, this can cause a big time investment that one might claim is not justified.
Benefits of TDD and BDD in Rails Development
- Early Bug Detection:
TDD and BDD catch bugs at an early stage of development, reducing the likelihood of critical issues arising in production. - Enhanced Code Quality:
Writing tests before code enforces well-structured, modular, and maintainable code, resulting in a more robust application. - Clear Documentation:
Test cases serve as clear documentation of the code’s intended behavior, making it easier for developers to understand and work with the codebase. - Collaboration:
BDD encourages collaboration between technical and non-technical team members, leading to a shared understanding of requirements. - Regression Prevention:
Automated tests created through TDD and BDD ensure that new changes do not break existing functionalities.
Best Practices for TDD and BDD in Rails
- Start Small:
Begin by writing tests for small, incremental features. This helps you master the TDD/BDD process and ensures a gradual buildup of test coverage. - Red-Green-Refactor:
Follow the TDD cycle religiously: write a failing test, make it pass with minimal code, then refactor to improve code quality. - Human-Readable Scenarios:
In BDD, use human-readable language to describe scenarios, making them understandable to all team members. - Automate Everything:
Automate your tests so that they can be executed frequently and consistently. - Maintain Test Suite:
Regularly maintain and update your test suite to reflect changes in requirements and keep it relevant.
Verdict
If you are the sole developer and a product owner too, then you should go for TDD. It’s easier for a technical person to understand, which is an advantage in keeping things scoped and under control. Thus keeps you out of messing up with RegExs for test steps. On the flip side, you should go with BDD, if you are building this for a client, and they are hands-on with regard to the specifications.
See Also : Security Checks you must do before Rails App release
Hope you liked it. Go ahead and post your comments what you think about this?
Related Questions
What is the fundamental principle behind Test-Driven Development (TDD) in Rails development?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) in Rails involves writing tests before writing the actual code. This approach ensures that the code meets the desired behavior defined by the tests.
The TDD cycle includes writing a failing test, writing the minimum code required to pass the test, and then refactoring the code for improved quality.
How does Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) differ from Test-Driven Development (TDD)?
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) extends the principles of TDD by focusing on the behavior of software from the user’s perspective.
BDD emphasizes collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define behavior using human-readable scenarios like “Given-When-Then.” BDD scenarios are translated into automated tests, serving as living documentation that ensures the software aligns with intended behaviors.
Q3: What benefits does Test-Driven Development (TDD) bring to Rails development projects?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) offers benefits such as early bug detection, enhanced code quality, clear documentation of desired behavior, collaboration among team members, and prevention of regressions.
TDD ensures that the codebase is well-structured, modular, and maintainable, leading to a more robust and dependable Rails application.
How can Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) foster effective collaboration in Rails development teams?
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) promotes collaboration by involving technical and non-technical team members in defining behavior scenarios.
Developers, testers, and business stakeholders work together to create human-readable scenarios that describe the software’s behavior. This shared understanding ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding the requirements and expectations.
What are some best practices for successfully implementing Test-Driven Development (TDD) and Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) in Rails projects?
Best practices for TDD and BDD include starting small by writing tests for incremental features, following the red-green-refactor cycle, using human-readable language for BDD scenarios, automating tests for frequent execution, and regularly maintaining and updating the test suite to reflect changes in requirements.
These practices ensure that TDD and BDD are effectively integrated into the development process, leading to high-quality Rails applications.