Introduction:
Finally, the most awaited Rails 4.0 version has been released by the Rails team on 25th of June. Rails 4 has got huge changes. There are tons of new features available, which can make your life as a Rails developer a lot easier. We will talk about the most exciting features in Rails 4 and why you should upgrade from Rails 3 version as soon as possible.
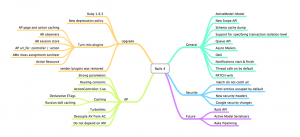
New features of Rails4
1. Ruby Versions
It is essential to note that Rails 4 would require Ruby 1.9.3 or higher, in fact Ruby 2.0.0 is recommended for your Rails 4 apps.
2. ‘Gemfile’
Rails now uses a ‘Gemfile’ in the application root to determine the gems you need for your app to start. This ‘Gemfile’ is processed by the Bundler gem, which then installs all the dependencies. It can also install all the dependencies locally to your app so that it doesn’t depend on the system gems.
Read Also: How to do tagging in Rails with gem ‘Acts_as_taggable_on’?
3. ‘Threadsafe’ by Default
Rails 4 will be thread-safe by default i.e. removing overhead and improving the performance on threaded servers, like thin and puma. You will have to ensure that your application and its dependencies are thread-safe, in other words, avoiding global state e.g. class or global variables.
4. No More vendor/plugins
Rails 4.0 will no longer support loading of plugins from vendor. You must replace any plugins by extracting them to gems and adding them to your ‘Gemfile’. If you choose not to make them gems, you can also move them into a different directory such as lib/my_plugin/* and add an appropriate initializer in config/initializers/my_plugin.rb.
5. New Testing Directories
The biggest change made to the testing of Rails 4 app is not the swapping of the testing framework, rather the testing folder structure. The test folder will now have a structure very similar to RSpec:
Developers will no longer have to worry if the test is “functional” or a “unit”. The structure provides a clear separation of where the tests in your application should go.
6. Strong Parameters
In Rails 4, a new pattern has been introduced to secure your models from mass assignment. You can filter the parameters passed to your model in the controller instead of ‘whitelisting’ the attributes in your model using “attr_accessible”.
[sourcecode]class PostController < ApplicationController
def create
@post = Post.create(params[:user])
end
end[/sourcecode]
You can protect against unexpected input with declarations in the model using “attr_accessible”.
[sourcecode]attr_accessible :title, :description[/sourcecode]
In Rails 4, you don’t need to worry about unexpected input attributes in your model anymore.
Strong Parameters gem moves user input into the controller.
[sourcecode]class PostController < ApplicationController
def create
@post = Post.create(post_params)
end
private
def post_params
params.require(:post).permit(:title, :description)
end
end[/sourcecode]
The “params hash” in your controller is not a normal hash. It’s actually an instance of ActionController::Parameters, which exposes the “require” and “permit” methods.
The “require” method ensures that the specified key is available in the “params” hash, and raises an ActionController::ParameterMissing exception if the key doesn’t exist.
The “permit” method protects you from unexpected mass assignment.
7. Renamed Callbacks
Action callbacks in controllers are now renamed from *_filter to *_action
Example:
[sourcecode]before_filter :before_action
arround_filter :arround_action
after_filter :after_action[/sourcecode]
All existing *_filter methods will still work with no deprecation warnings. However, It would recommend to replace of *_filter calls to *_action
8. Rails 2 Model.find(:[all|:first:last]) syntax is now deprecated.
9. Deprecated dynamic finders
Rails 4 deprecates all dynamic finder methods (with the exception of find_by and find_by_…). Instead, you’ll use where
[sourcecode]find_all_by_… => where(…)
scoped_by_… => where(…)
find_last_by_… => where(…).last
find_or_initialize_by… => where(…).first_or_initialize
find_or_create_by… => where(…).first_or_create
find_or_create_by_…! => where(…).first_or_create![/sourcecode]
The deprecated finders gem will be included as a dependency in 4.0 and removed in 4.1. The gem, however, will be around and maintained until 5.0.
10. Queuing system
Rails4 added the support for a queue to run background jobs. The queuing API is very simple. The ActiveSupport::Queue class comes with a push method that accepts any object, as long as that object defines a run method.
Example
Let’s say that you have a job class TestJob that prints the name of an author
[sourcecode]class TestJob
def run
puts "I am running!"
end
end[/sourcecode]
You can queue a job to print “I am running!” in the background by pushing an instance of that class to Rails.queue:
[sourcecode]Rails.queue.push(TestJob.new)
"I am running!"[/sourcecode]
The job will run in a background thread and it will not block any of your operations.
11. Live Streaming
Live Streaming is a major new feature in Rails 4. It facilitates you to stream data to the browser. Enabling live streaming requires you to mix in the ActionController::Live class in your controller.
[sourcecode]class MyController < ActionController::Base
include ActionController::Live
def stream
response.headers[‘Content-Type’] = ‘text/event-stream’
100.times {
response.stream.write "hello world\n"
sleep 1
}
response.stream.close
end
end[/sourcecode]
It will stream the string “hello world” to your client 100 times.
You should take notice of following things
- Manually close the stream after you are done streaming in the browser.
- Headers must be written first before writing anything to the client.
- You will need a concurrent Ruby web server, such as puma.io, Rainbow or Thin. Using the default ‘WEBrick’ server won’t work, since it buffers all the output. Also note that Unicorn won’t work either, since it kills the connection after 30 seconds.
- All controllers that include ActionController::Live would be executed in another thread, so make sure your code is thread-safe.
12. Rails 4 and Hstore from Postgres 9.2
ActiveRecord in Rails 4 will now support the PostgreSQL hstore extension. This database extension allows a new data type for a column in PostgreSQL called ‘hstore’ which effectively represents a string-only hash. For most purposes this would be similar to serializing data in a text column, but the fact that this is now a native datatype, it would grant a huge performance boost and the capability to query against it directly. You can now have a hint of a schema-less database available to your application without needing to perform a full upgrade to MongoDB, CouchDB, Riak or other similar schema-less data store.
13. Cache Digests (Russian Doll Caching)
Make it super easy to do Russian Doll-caching through key-based expiration with automatic dependency management of nested templates
14. Turbolinks
Now you can speed-up the client-side with ‘Turbolinks’. It essentially turns your app into a single-page ‘JavaScript’ application in terms of speed, but with none of the developmental drawbacks (except, maybe, compatibility issues with some existing JavaScript packages).
15. Routing Concerns
In Rails 4, routing concerns has been added to the router. The basic idea is to define common sub-resources (like comments) as concerns and include them in other resources/routes.
16. Rails3 code
[sourcecode]resources :posts do
resources :comments
end
resources :articles do
resources :comments
resources :remarks
end[/sourcecode]
In rails4 the concern routes will only be included within a resource by passing it to the routing option :concerns. The :concerns option can accept one or more concerns.
[sourcecode]concern :commentable do
resources :comments
end
concern :remarkable do
resources :remarks
end
resources :posts, :concerns, :commentable
resources :articles, :concerns =>[:commentable, :remarkable][/sourcecode]
Why we should upgrade to rails4?
Rails4 is recommended to be used with Ruby 2.0.0. It stopped supporting Ruby 1.8.x after Rails 3.2. Ruby 1.9.2+ will be supported until Rails 5 is released!
Aware of any other not-so-obvious features? Please post it in the comments below.