WordPress is a free and powerful software to develop websites. It’s a CMS (Content Management System) for managing content without getting involved in the complexities of the web architecture. It is very simple and easy to use, even for beginners.
41.4% of the top 10 million websites & 60% of all CMS are powered by WordPress. These impressive stats continue to dominate the web-development industry.
In 2003, it started as a blogging tool, now it has become the platform to build any kind of website.
Everyone is talking about WordPress these days. Its many effective features have made it the favorite among many big brands.
This platform is leading the market. The popular brands like Bloomberg, TechCrunch, BBC America, are using this CMS as their core web platform
Agencies are also recommending this for business websites, because they are well aware of the wordpress cms development services.
But why is there so much demand around this platform?
Here you go.
What is WordPress?
“WordPress.com is the only service of its kind that not only lets you export your data, but gives you an open source package you can run on pretty much any web host out there to run your own instance of the software. So the freedom is really in your hands.”
– Matt Mullenweg, CEO of Automattic Inc.
WordPress is a CMS or a Content Management System that developers use as a framework o create web applications/portals.
This simple CMS can be used by anyone, you can modify and make the necessary changes. To use it you don’t need any technical knowledge.
This framework is not only used to develop websites but it is the best blogging platform.
It is also a Marketing tool. So this helps to easily get noticed among your customers and rank in search engines.
Never miss an update for us. Join 10,000+ marketers and leaders.
Why use WordPress Website?
Everyone wants to have a place in this ever-growing digital world. Gone are the days when one must know how to code to put their website online by building everything from scratch. WordPress theme services makes it too easy to start building a site with just a few clicks.
WordPress is not only used to build web pages faster but also to manage the content effectively. Whether it’s a one-page blog or an eCommerce marketplace, WordPress is the one-stop solution for everything.
“At present there are more than 74 million websites that are developed using WordPress. This website uses WordPress to post new content every hour.” – The ThemeForest
Also, the use of WordPress highly depends on it’s easy to use features. Including this WordPress provides many effective features which make this framework more and more popular.
“Using WordPress is a no-brainer. There’s a reason 34% of the web uses it.” by Kinsta
Everything from big platforms like Squarespace to Wix are some of the wonderful tools. But here we will describe why use WordPress over these tools to develop your website.
Do you want a WordPress website but don’t know how to create one? We will install and setup WordPress for you, absolutely free of cost!
- Use it for free
- Easy to use
- It rules the CMS market
- Google friendly
- Adaptability
- Safe and secure
- Multi- user Ability
- Big Brands use WordPress
- Supports Multimedia
 (Source: Webster Digital Marketing)
(Source: Webster Digital Marketing)
1. Free to use
Yes, WordPress doesn’t cost a penny to try. Whether you are creating a commercial site or a personal blog, with this it doesn’t cost you a penny.
Download and install it locally on your system and start using it straight away. Understanding the dashboard and various ways to edit & publish content is what WordPress is all about.
There is a huge collection of per-build themes and plugins to test out.
It is one of the reasons why people use it more.
Once you get to know the workflow, it’s time to go online by just buying a domain name and a hosting service depending on the scale of the website.
 (Source: Wpbeginner)
(Source: Wpbeginner)
As WordPress framework is an open-source, you can alter or develop the source code the way you like, customize the website functionality and the overall look.
Although it is free, you need to spend some amount for other features. However, the premium paid ones provide numerous features to your websites.
2. Easy to use
Most businesses suggest the use of WordPress because it’s easy to use. It comes with easy to install templates that are available with complete customizable code.
It has an editing interface that requires no HTML experience for any changes, to alter the layout and more features to create any changes into your WordPress website.
You can update your company information, product information, or modify content on your website using this, by following some easy steps.
Never miss a single post from Andolasoft.
Join 10,000+ others who get our weekly post with insider tips!.
3. It rules the CMS market
It is not just a popular CMS, it creates more competition.
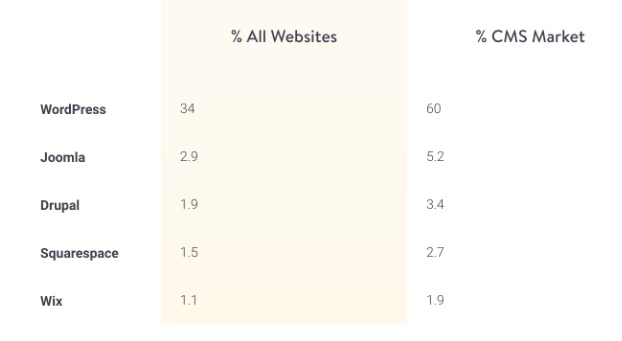 (Source: quicksprout.com)
(Source: quicksprout.com)
According to the usage statistics from W3Techs more than 59.5% of all websites that choose Content Management Systems use WordPress.
It has a huge percentage of market share. Along with the market share the large number of supportive tools help this framework to become more efficient and effective.
4. Google Friendly
As this is a CMS based framework, Google and other search engines crawl into these websites that help to rank. Most businesses developed their website using this framework, to take this advantage of WordPress.
To get ranked in Google is the main motto of every website. With this website you can easily enjoy this advantage of WordPress.
Some of the experts say, using the WordPress framework can boost your ranking.
There are plugins that optimize the pages to drive more traffic. If you don’t know anything about SEO, just install the recommended powerful SEO plugins with few basic settings and WordPress will take care of its own.
5. Adaptability
It is also flexible to customize. You can accommodate your website using the extensions and Plug-in.
Whether you are using WordPress for your personal use or for creating a small business website or for a large business website doesn’t matter.
By using this framework you can customize and add extensions to your website according to your choice.
You get total control on the coding. So it can be easily customized to any per-made themes and design.
Never miss a single post from Andolasoft. Join 10,000+ others who get our weekly post with insider tips!.
6. Safe and Secure
Security is given first priority when it comes to WordPress development and rightly so. No matter how easy it is to build anything, it is unacceptable for any platform to compromise with security. WordPress implements every security measure to prevent any possible breach of information and stay protected.

The popularity of WordPress website design has gained the interest of hackers.
So, to control this issue the core team of WordPress software has strengthened the security measures.
According to a Q3 2017 study by Sucuri, a multi-platform security company,
“WordPress continues to lead the infected websites they worked on at 83%. This is up from 74% in 2016.”
This CMS has taken strong security measures to preserve its user’s trust. For high-level security, it is recommended to install security plugins and keep updating it with the latest updates. Security plugins automatically generate cryptic passwords and implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) which are too hard for hackers to crack.
This CMS has taken strong security measures to preserve its user’s trust.
However, the users need to be more careful while downloading the WordPress plug-ins from any trusted source.
7. Multi-User Ability
It works best for multi-users. If your team size is large or has multiple teams, freelancers, agencies who are working on your websites and you need to give access to them.
With this you get total control over those who get access to your Business website. You can develop new accounts, by giving specific permissions to the accessibility of user’s and keep them out of the area that is required.
The permissions include:
- Admin
- Super Admin
- Author
- Editor
- Subscriber
- Contributor
8. Big Brands Use WordPress
It has power to more than 35% of all websites. There are around 1.7 billion sites using WordPress.
Every hour there are thousands and more content that are delivered to the site visitors by using this.
It has not remained limited to only small to medium-sized businesses. Many popular brands suggest the use of WordPress for their websites.
Some of the big brands are- Etsy Journal, TechCrunch, Microsoft News, TED Blog, PlayStation, BBC America, Walt Disney Company, Skype, Star Wars Blog, yelp and more.
Andolasoft has also developed its Blog site through WordPress.
9. Supports Multimedia
Adding media files to your websites has become a necessity now-a-days. With media files attached, it creates more traffic.
With the uses of blogs and various content, you can add various types of multimedia. Any type of media files can be added such as Audio, Images, Documents, and Video.
You need to add high quality images and videos to your websites for better engagement and google ranking.
10. Bloggers paradise
Initially built as a blogging platform, WordPress still holds firm to its roots. It leads the race to be the most preferred blogging platform.
 (Source: wordpress.org)
(Source: wordpress.org)
Because it is literally painless to create, edit, publish and manage blogs using the set of tools inside the popular blog editor. The drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to handle media contents too.
The blog owner can set different permissions for different user roles.
Finally, WordPress has a feature called taxonomies, that lets the blog creator add categories and tags to a content, which helps the reader to navigate to contents that are similar and inter-linked.
11. Responsive flawless experience
More than 60% of web content is viewed on phones. So, it’s very important to create websites that are device friendly. WordPress automatically detects the types of device and renders the content accordingly.

Google says,
“Mobile-friendly sites show up higher in search results and if your site isn’t mobile-friendly, visitors are 5 times more likely to leave.”
Responsive Web Design (RWD) is one of the most important considerations for developers in web development. WordPress has in-build options to simultaneously design web pages of different screen sizes whether it is a desktop, a laptop, a tablet, or a mobile phone.
What Ways do you need to follow to Use WordPress?
WordPress means you can create any type of business website.
Starting from a simple website to an eCommerce marketplace or for the personal blog, for any purposes, this framework helps you with this.
Here are some examples of different websites you can create with this:
- Online Store
- Blogging
- Membership Website
- Online Courses
- Online Marketplace Websites
- Podcast Website
- Dropshipping Website
- Coupon Website
- Affiliate Website
- Online Forum Websites
- Social Networking Websites
So, these are some of the websites that you can create using this framework.
I’ve worked with the team at AndolaSoft on multiple websites. They are professional, responsive, & easy to work with. I’ve had great experiences & would recommend their services to anyone.
Ruthie Miller, Sr. Mktg. Specialist
Salesforce, Houston, Texas
LEARN MORE
FAQ:
What is WordPress?
This is a Content Management System that is used to develop websites. It is also available in Open source and .com. So anyone can develop any kind of website.
How to build a WordPress website?
With this you can develop a business website and use it as a blogging platform. You need to follow these steps:
- Sign up for a web Hosting
- Choose a domain name for your website
- Install free WordPress software
- Select a WordPress theme
- Develop your first page
- Install all the essential plugins to your WordPress website
- And then start marketing your website
What is WordPress used for?
With this you can develop your own website. WordPress custom theme works by combining various core files. Files are added, installed and database. It provides dashboards that let you manage the entire work.
Is WordPress easy for Beginners?
It is a simple to use tool. Even beginners can use it very easily. It is easy to set up and run. Several web hosts come with what are called as one-click auto-installers. It is simple to use, unlike Microsoft.
Is WordPress Free to use?
This core software is free to use. You can download it for free and use it for any way you want to. You can customize it, extend it, redistribute it or it can also be sold until you use it as GPL License.
Conclusion:
WordPress framework is a powerful content management system. It is strongly followed globally to develop many amazing websites.
It provides you with complete control over your website. This web application provides great advantages like plugins, free tools, and themes with full media support.
With more content, demands more maintenance and scaling it is as simple as a new WordPress website. It is advisable to frequently back-up your entire website in case of any unfortunate accidental loss of data. It also supports 169 languages worldwide.
Automattic, the company behind WordPress has even bigger plans in future. It has come a long way since its inception and has experienced exponential growth. Since then it has created a world of its own. We have concluded that, with WordPress, possibilities are endless.
The best way to experience these features is by using them. Let us help you build your website.
So you can enjoy your business and develop your website using Andolasoft.
Your current host might charge you extra cost and time, get it back with Andolasoft.
Well professional wordpress developers will help you develop your own websites according to your preferences at an affordable range.
Want to develop your own business websites, contact us to hire our developers to design your professional websites.
If you like this article then please subscribe to our blog for such amazing articles.