A framework is a structure that developers choose to build their application. It determines the structure of the application and facilitates it to connect with many different API’s. A proficient PHP framework enables developers to develop PHP application faster, efficiently and assist in building stable applications thereby reducing the amount of repetitive coding for PHP programmers.
Frameworks provide scaffolding features that facilitates the development team to build faster and cleaner application. They often provide tool sets for both the UI components and the database access.
Note: It is advisable to use the latest stable version of a framework.
Never miss an update from us. Join 10,000+ marketers and leaders.
Here are few aspects of a proficient PHP framework:
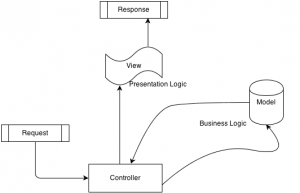
MVC Architecture:
- The framework should make use of Model View Controller (MVC) architecture. Some of the best frameworks also provide libraries, plug-ins, helpers, and extensions to assist developers. It would be smart and efficient to employ a framework that has at least two of these options.
Database Support:
- It is one of the most crucial aspects of every PHP development framework. You need decide your framework depending on the database you are going to use for your web application.
For Example: ‘CodeIgniter’ supports MySQL, Oracle, and SQLite, whereas the ‘Kohana’ framework doesn’t.
Community & Documentation:
- The framework should be supported by a strong community, not just in terms of size but also in terms of activity and usefulness. Even if it’s a small community, you should be able to get ample support from the community.
A PHP framework should also have good documentation. It should be comprehensive and up-to-date.
Below, I have provided a list of some popular and commonly used PHP frameworks.
CakePHP 2.x:
- CakePHP is a rapid development framework for PHP. It’s a foundational structure for programmers to create web applications. CakePHP has an active developer team and community, bringing great value to the project. It is also the most preferred development framework.
Source:http://book.cakephp.org/2.0/en/index.html
Symfony 2.x:
- Speed up the creation and maintenance of your PHP web applications. Replace the repetitive coding tasks by power, control and pleasure.
Source: http://symfony.com/
CodeIgniter 2.x:
- CodeIgniter is a powerful PHP framework with a very small footprint, built for PHP coders who need a simple and elegant toolkit to create full-featured web applications.
Source: http://ellislab.com/codeigniter
Zend Framework 2:
- It is an open source framework for developing web applications and services using PHP 5.3+. Zend Framework 2 uses 100% object-oriented code and utilizes most of the new features of PHP 5.3, namely namespaces, late static binding, lambda functions and closures.
- Zend Framework 2 evolved from Zend Framework 1, a successful PHP framework with over 15 million.
Source: http://framework.zend.com
Yii Framework 1.1.x:
- Yii comes with rich features: MVC, DAO/ActiveRecord, I18N/L10N, caching, authentication and role-based access control, scaffolding, testing, etc. It will reduce your development time significantly.
Source: http://www.yiiframework.com
Kohana 3.x:
- An elegant HMVC (Hierarchical model–view–controller) PHP5 framework that provides a rich set of components for building web applications.
Source: http://kohanaframework.org/
FuelPHP:
- It is a simple, flexible, community driven PHP 5.3+ framework, based on the best ideas of other frameworks.
Source: http://fuelphp.com/
There are a number of PHP development frameworks in the market which enables the development team to do more with the programming language. Development frameworks makes coding for PHP more manageable and programmers can take its advantage by making use of a convenient development framework.