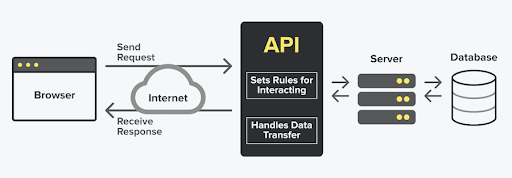
PHP, the versatile scripting language, has been powering dynamic web applications for decades. With the evolution of web development, PHP frameworks have emerged as indispensable tools that streamline the development process, enhance code organization, and boost efficiency.
If you are enthusiastic about developing stunning PHP web applications you have come to the right place. In this blog we will discuss comprehensively about the various development frameworks, explore its benefits and also outline the top 10 best PHP development frameworks in 2023.
What is PHP Framework?
A framework is a pre-built collection of libraries, tools, and templates designed to facilitate web application development. It provides PHP developers with a structured environment, enforcing best practices, reducing repetitive tasks, and ensuring scalability and maintainability of the codebase.
Why Use PHP Frameworks?
- Rapid Development:
Frameworks provide pre-built components, modules, and libraries that accelerate development time. This means you can focus on building unique features rather than writing repetitive code. - Code Reusability:
Frameworks encourage the creation of reusable code components. This promotes consistency, reduces redundancy, and simplifies maintenance. - Structured Architecture:
Most frameworks follow a structured architecture, such as the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. This separation of concerns enhances code organization, making it easier for PHP development service providers to manage and scale applications. - Security Enhancements:
Frameworks come equipped with built-in security measures, such as input validation, SQL injection prevention, and protection against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. This significantly reduces vulnerabilities and enhances the overall security of your application. - Scalability:
Frameworks offer tools and guidelines that enable PHP development companies to build scalable applications. As your user base grows, your application can handle increased traffic and functionality without significant architectural changes. - Community Support:
Most popular frameworks have active and vibrant communities. This means you can find tutorials, guides, documentation, and plugins readily available. Community support facilitates problem-solving and encourages continuous learning. - Consistent Coding Standards:
Frameworks often enforce coding best practices and standards. This ensures that your code is clean, maintainable, and adheres to industry standards. - Database Abstraction:
Frameworks typically offer tools for database abstraction, making it easier to work with various database systems. This minimizes the effort required to switch between databases or update your application’s data structure. - Testing and Debugging:
Frameworks often come with built-in testing tools and debugging support. This helps you identify and rectify issues more efficiently, leading to a more stable and reliable application. - Future Compatibility:
As PHP evolves, frameworks are updated to incorporate new features and security enhancements. Using a framework ensures your application stays compatible with the latest PHP versions, reducing the risk of outdated code.
Top Things To Consider When Choosing a PHP Development Framework
- Project Requirements:
Understand the specific requirements of your project. Consider factors like project size, complexity, scalability needs, and the type of application you’re building (web app, API, content management system, etc.). - Learning Curve:
Evaluate your team’s familiarity with different frameworks. Opt for a framework that aligns with your team’s skill levels, as some frameworks may have steeper learning curves than others. - Documentation:
Check the quality and comprehensiveness of the framework’s documentation. Clear documentation is essential for efficient development and troubleshooting. - Community Support:
A robust and active PHP community can provide valuable resources, plugins, tutorials, and solutions to common challenges. Look for frameworks with thriving communities that can support your development journey. - Performance:
Consider the framework’s performance benchmarks and how they align with your application’s speed and responsiveness requirements. Certain frameworks may be more suitable for high-traffic applications than others. - Architecture and Features:
Assess the architecture and features offered by the framework. Does it follow a Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern or another architecture? Does it include features that align with your project’s needs, such as authentication, caching, or RESTful API support? - Security Features:
Security is paramount for any application. Evaluate the framework’s built-in security features, such as input validation, protection against SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS) prevention. - Scalability:
Choose a framework that allows your application to grow without significant architectural changes. Ensure the framework’s structure supports scalability and doesn’t hinder future expansion. - Ecosystem and Integrations:
Consider the framework’s ecosystem and compatibility with other tools you might use, such as databases, front-end libraries, and third-party APIs. - Community Feedback:
Research user reviews and feedback from developers who have used the framework. Their experiences can provide insights into the framework’s strengths, weaknesses, and real-world performance. - Longevity and Updates:
Choose a framework that is actively maintained and updated. This ensures that your application remains compatible with the latest PHP versions and industry trends. - Vendor Lock-In:
Be cautious of frameworks that tie you into proprietary tools or technologies, potentially limiting your flexibility in the future. - License and Cost:
Understand the licensing terms of the framework. Some frameworks are open-source, while others may have commercial licenses or additional costs for specific features. - Flexibility vs. Convention:
Consider whether you prefer a framework that enforces a strong coding structure and conventions or one that offers more flexibility for custom solutions. - Community Contributions:
Frameworks with a strong community of contributors often offer a broader range of plugins, extensions, and packages that can enhance your development process.
What Are the Best PHP Frameworks in 2023?
-
Laravel
Laravel is a modern PHP framework known for its elegant syntax, developer-friendly environment, and robust ecosystem. follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern and provides features like Blade templating, Eloquent ORM, and artisan command-line tool.
Pros:
- Elegant and expressive syntax that’s easy to learn and read.
- Extensive documentation and a thriving community with ample resources.
- Built-in features like authentication, routing, caching, and more.
- Eloquent ORM simplifies database management and relationships.
- Powerful Blade templating engine for efficient Laravel front-end development.
Cons:
- Slightly steeper learning curve for beginners due to its rich feature set.
- Heavier footprint compared to micro-frameworks, which might impact performance in certain scenarios.
-
Symfony
Symfony is a robust PHP framework known for its high flexibility, reusable components, and emphasis on best practices. It provides a collection of components that can be used independently or as part of a full-stack framework.
Pros:
- Highly customizable framework with a modular architecture.
- Reusable components allow for flexibility and optimized development.
- Well-documented and follows strict coding standards.
- Strong emphasis on testing and robust security features.
- Active community support and long-term stability.
Cons:
- Requires a solid understanding of PHP and object-oriented programming.
- Learning curve can be steep for beginners due to its extensive features.
-
CodeIgniter
CodeIgniter is a lightweight and user-friendly PHP framework that’s ideal for small to medium-sized projects. It emphasizes simplicity and speed, making it a popular choice for rapid development.
Pros:
- Minimal setup and straightforward documentation.
- Excellent performance due to its lightweight footprint.
- Flexibility for custom PHP app development without imposing too many conventions.
- Active community and user-friendly environment, suitable for beginners.
Cons:
- Fewer built-in features compared to other frameworks, which may require third-party libraries.
- Not as suitable for large-scale applications due to its simplicity.
-
Yii
Yii is a high-performance PHP framework designed for web 2.0 applications. It follows the MVC pattern, comes with powerful caching support, and offers various features that expedite development.
Pros:
- Fast performance and robust caching mechanisms.
- Follows strict security practices with built-in authentication and authorization.
- Powerful code generation tools streamline development.
- Extensible and suitable for building both small and large applications.
- Active community and continuous updates.
Cons:
- Smaller community compared to Laravel or Symfony.
- Learning curve for beginners due to its advanced features and concepts.
-
Phalcon
Phalcon is a unique PHP framework implemented as a C extension. This design choice contributes to its exceptional performance and low resource consumption.
Pros:
- Outstanding performance due to its C extension architecture.
- Lower memory consumption compared to other frameworks.
- Rich set of features including ORM, caching, validation, and more.
- Detailed documentation and active community.
- Suitable for high-traffic applications and resource-intensive tasks.
Cons:
- Requires compiling the extension, making deployment slightly more complex.
- Smaller community compared to more established frameworks.
-
Slim
Slim is a micro-framework designed for simplicity and flexibility. It’s suitable for building APIs, small web applications, and prototyping.
Pros:
- Minimalistic design and lightweight footprint.
- Ideal for small projects and quick prototyping.
- Excellent choice for building RESTful APIs.
- Easy to learn, making it beginner-friendly.
- Customizable and adaptable to specific project needs.
Cons:
- Limited built-in features compared to full-stack frameworks.
- Not suitable for complex applications or projects requiring extensive features.
-
Laminas
Laminas (previously Zend Framework) is a versatile PHP framework that offers a collection of professional-grade components for building robust applications.
Pros:
- Modular architecture allows for flexible use of components.
- Suitable for both small and large applications.
- Emphasis on code quality, best practices, and security.
- Extensive documentation and strong community support.
- Smooth transition from Zend Framework to Laminas.
Cons:
- Requires some understanding of design patterns and best practices.
- Learning curve for beginners due to its modular nature.
-
Phinx
Phinx is a database migration tool that’s often used in conjunction with PHP frameworks to manage database schema changes over time.
Pros:
- Simplifies database migrations and version control.
- Supports various databases, making it versatile.
- Command-line interface provides a user-friendly experience.
- Easily integrates with popular PHP frameworks.
- Efficiently handles changes to database schemas in collaborative projects.
Cons:
- Designed specifically for database migrations and not a full PHP framework.
- Might require additional tools or components for complete application development.
-
CakePHP
CakePHP is a modern PHP framework that emphasizes rapid development and convention over configuration. It follows the MVC architecture and offers features that promote code reusability. CakePHP is one of the best frameworks for eCommerce development. We have compiled a detailed blog on how to build an eCommerce application using CakePHP.
Pros:
- Rapid development with conventions that reduce configuration.
- Built-in features like CRUD operations, authentication, and more.
- Simple and readable syntax that’s beginner-friendly.
- Active community and continuous updates.
- Suitable for building applications of various sizes.
Cons:
- Less flexible compared to some other frameworks due to its strict conventions.
- Learning curve for beginners who are new to conventions.
-
FuelPHP
FuelPHP is a flexible and modular PHP framework designed for rapid application development. It aims to provide a balance between simplicity and functionality, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced PHP developers.
Pros:
- Modular architecture allows developers to use only the components they need.
- Emphasizes security with features like input validation, XSS filtering, and CSRF protection.
- ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) simplifies database operations and relationships.
- Robust routing system for handling URLs and requests.
- Active community and user-friendly documentation.
Cons:
- Smaller community compared to more popular frameworks.
- Fewer built-in features compared to larger frameworks like Laravel.
- Limited resources and plugins compared to more established frameworks.
-
Fat-Free Framework (F3)
Fat-Free Framework, often referred to as F3, is a lightweight PHP framework known for its minimalistic design and fast performance. It aims to provide essential features without unnecessary overhead.
Pros:
- Extremely lightweight with minimal overhead.
- Ideal for building small web applications and APIs.
- Simplicity in design and syntax, making it easy to learn.
- Modular and extensible architecture.
- Good performance due to its minimalist approach.
Cons:
- Limited built-in features compared to full-stack frameworks.
- May not be suitable for large-scale applications with complex requirements.
- Smaller community compared to more widely used frameworks.
In conclusion, PHP frameworks offer a host of advantages that streamline development, enhance security, and improve the overall quality of web applications. Whether you’re building a small website or a complex web application, leveraging a PHP framework can significantly boost your productivity and the quality of your final product.
FAQs
Which PHP framework is the best for beginners?
Frameworks like CodeIgniter, Laravel, and Slim are often recommended for beginners due to their user-friendly environments, clear documentation, and ease of learning.
Which PHP framework is best for large-scale applications?
Symfony, Laravel, and Yii are commonly used for large-scale applications due to their robust architectures, scalability features, and extensive libraries.
What is the advantage of using a modular PHP framework?
Modular frameworks like Symfony and Laminas allow PHP developers to use specific components independently, offering greater flexibility and optimizing resource usage.
Is there a PHP framework that focuses on minimalism?
Fat-Free Framework (F3) is designed with minimalism in mind, offering essential features without unnecessary overhead, making it ideal for small applications and APIs.
Can I switch PHP frameworks once my project has started?
While it’s possible, switching frameworks midway through a project can be time-consuming and require significant code changes. It’s best to choose the right framework at the outset.