In today’s data-driven economy, organizations generate more data than ever before. According to industry research, enterprises analyze less than 30% of the data they collect, leaving valuable insights untapped. This challenge has made analytics-driven decision-making a boardroom priority.
However, one critical confusion persists across leadership teams: BI vs Data Analytics. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct business purposes, operate at different levels of maturity, and answer fundamentally different questions.
Understanding the difference between BI vs Data Analytics is no longer optional. For CTOs, founders, and product leaders, this clarity directly impacts investment decisions, platform selection, team structure, and long-term scalability.
In this blog, you’ll learn the top 10 differences between BI vs Data Analytics, real-world use cases across industries, best practices for implementation, and how organizations can combine both for maximum impact. You’ll also see how Andolasoft, with deep expertise in BI, AI, machine learning, and data analytics, helps businesses design future-ready data ecosystems that drive measurable outcomes.
Business Need & Importance of Understanding BI vs Data Analytics
Modern organizations operate in an environment defined by speed, competition, and constant change. As a result, leadership teams need accurate insights, predictive intelligence, and real-time visibility to stay ahead. This is where understanding BI vs Data Analytics becomes critical.
Why This Distinction Matters Today
Business Intelligence focuses on what has already happened, while Data Analytics goes further to explain why it happened and what is likely to happen next. Companies that fail to distinguish between the two often invest in tools that don’t align with their goals, resulting in low adoption and poor ROI.
Industry-Wide Challenges
- Healthcare organizations struggle with historical reporting but need predictive analytics for patient outcomes and capacity planning.
- eCommerce companies rely on BI dashboards for sales tracking but require advanced analytics for personalization and demand forecasting.
- Logistics and supply chain firms need BI for operational visibility, yet analytics for route optimization and risk prediction.
- Fintech and SaaS companies depend on BI for compliance reporting while using analytics for fraud detection and churn reduction.
- Manufacturing enterprises use BI for production reporting and analytics for predictive maintenance.
Risks of Not Modernizing
Organizations that rely only on legacy BI or fragmented analytics face serious risks:
- Delayed decision-making due to static reports
- Revenue loss from missed predictive opportunities
- Operational inefficiencies and higher costs
- Poor customer experiences due to lack of personalization
- Inability to scale analytics across teams
Therefore, businesses need strategic, integrated data platforms instead of patchwork tools. This is where a trusted technology partner like Andolasoft plays a vital role in aligning BI vs Data Analytics with business objectives.
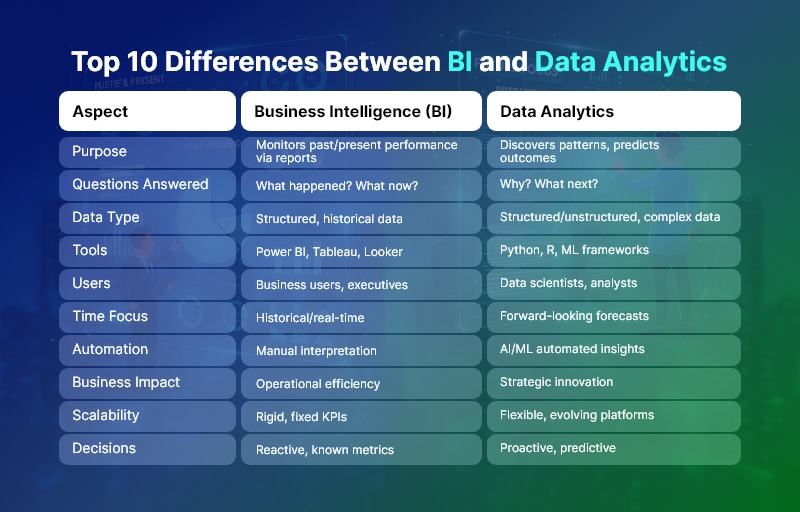
Top 10 Differences Between BI vs Data Analytics
1. Purpose and Core Objective
- Business Intelligence (BI) primarily focuses on monitoring past and present performance through dashboards, KPIs, and standardized reports.
- Data Analytics, on the other hand, aims to discover patterns, uncover root causes, and predict future outcomes using advanced analytical techniques.
2. Type of Questions Answered
- BI answers “What happened?” and “What is happening now?”, enabling descriptive insights.
- Data Analytics answers “Why did it happen?” and “What will happen next?”, enabling diagnostic and predictive insights.
3. Data Complexity and Depth
- BI works best with structured, clean, and historical data from data warehouses.
- Data Analytics handles large, complex, and unstructured datasets, including logs, text, IoT data, and behavioral data.
4. Tools and Technologies Used
- BI relies on tools like Power BI, Tableau, Looker, and Superset for visualization and reporting.
- Data Analytics uses Python, R, SQL, Spark, ML frameworks, and AI models for deep analysis.
5. User Base and Skill Requirements
- BI is designed for business users, executives, and operational teams with minimal technical skills.
- Data Analytics is driven by data analysts, data scientists, and engineers with strong statistical and programming expertise.
6. Time Orientation
- BI is historical and real-time, focusing on trends and current performance.
- Data Analytics is forward-looking, emphasizing forecasting, simulation, and optimization.
7. Level of Automation
- BI dashboards require manual interpretation and predefined metrics.
- Data Analytics enables automated insights, anomaly detection, and recommendations through AI and ML.
8. Business Impact Scope
- BI supports operational efficiency and management reporting.
- Data Analytics drives strategic transformation, innovation, and competitive advantage.
9. Scalability and Flexibility
- BI solutions are often rigid, built around fixed KPIs.
- Data Analytics platforms are highly scalable and flexible, evolving with business needs.
10. Decision-Making Power
- BI enables reactive decision-making based on known metrics.
- Data Analytics empowers proactive and predictive decision-making with higher accuracy.
Best Practices, Frameworks & Actionable Tips for BI vs Data Analytics
Step-by-Step Recommendations
- Define business objectives first, then decide whether BI, Data Analytics, or both are required.
- Establish a single source of truth using centralized data warehouses or data lakes.
- Adopt modular architectures that allow BI and analytics to coexist seamlessly.
Best Practices
- Standardize KPIs for BI to ensure consistency across teams and departments.
- Invest in data quality and governance, as analytics accuracy depends on clean data.
- Enable self-service BI while maintaining controlled access to advanced analytics.
Frameworks & Architectures
- Modern Data Stack (ETL/ELT, cloud data warehouse, BI layer, analytics layer).
- Lakehouse Architecture for combining BI reporting and advanced analytics.
- MLOps frameworks to operationalize analytics models at scale.
Do’s and Don’ts
- Do align BI dashboards with business outcomes, not vanity metrics.
- Do not overcomplicate BI with unnecessary analytics models.
- Avoid siloed tools that prevent data sharing across teams.
Quick Wins
- Automate recurring BI reports to save time.
- Introduce predictive analytics for high-impact use cases like churn or demand forecasting.
How Andolasoft Helps
Andolasoft enables organizations to implement BI vs Data Analytics effectively through:
- Custom Web & Mobile Development for analytics-driven applications
- SaaS Product Engineering with embedded BI and analytics
- BI, AI & Machine Learning Solutions for predictive intelligence
- Data Analytics & Application Modernization for legacy systems
- DevOps, Cloud & Automation for scalable performance
Choosing Andolasoft ensures faster implementation, lower risk, and measurable business value.
Customer Success
For example, a mid-sized healthcare SaaS provider, partnered with Andolasoft to modernize its reporting and analytics platform. Initially, the company relied solely on BI dashboards to track patient engagement and operational metrics.
Andolasoft implemented a unified BI vs Data Analytics solution, combining real-time dashboards with predictive analytics models. Within four months, achieved:
- 35% faster reporting cycles
- 25% reduction in operational inefficiencies
- Improved patient outcome predictions by 40%
- Higher adoption of analytics across leadership teams
By integrating BI for visibility and Data Analytics for prediction, transformed decision-making from reactive to proactive.
Key Takeaways & Closing
Understanding the difference between BI vs Data Analytics is essential for modern businesses.
- BI delivers clarity on past and present performance.
- Data Analytics unlocks predictive and prescriptive intelligence.
- Together, they create a powerful foundation for data-driven growth.
Organizations that adopt both strategically gain better visibility, smarter decisions, and sustainable competitive advantage. With the right partner, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and maximize ROI.
Andolasoft brings proven expertise in BI vs Data Analytics, helping organizations design, build, and scale intelligent data solutions that drive real outcomes.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between BI vs Data Analytics?
BI focuses on historical reporting and dashboards, while Data Analytics emphasizes predictive and diagnostic insights using advanced techniques.
2. Can BI and Data Analytics work together?
Yes. Combining BI vs Data Analytics enables organizations to track performance and predict future outcomes effectively.
3. Which is better for executives: BI or Data Analytics?
Executives typically rely on BI for quick insights, while analytics supports strategic forecasting and long-term planning.
4. Is Data Analytics more expensive than BI?
Data Analytics often requires more skilled resources, but it delivers higher strategic value when implemented correctly.
5. Do small businesses need BI vs Data Analytics?
Yes. Even small businesses benefit from BI dashboards and targeted analytics for growth and efficiency.
6. How does Andolasoft help with BI vs Data Analytics?
Andolasoft designs end-to-end BI and analytics solutions, from data engineering to AI-driven insights.
7. When should a company move beyond BI to Data Analytics?
When businesses need forecasting, automation, and deeper insights beyond descriptive reporting, Data Analytics becomes essential.
