Predictive BI is reshaping how organizations anticipate market trends, customer behaviors, and operational bottlenecks.
According to a recent Gartner report, companies adopting predictive intelligence can improve decision-making speed by up to 50%.
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, traditional reporting is no longer enough.
Leaders now require real-time forecasting to stay ahead — making Predictive BI: Transforming Raw Data Into Future Insights more urgent than ever.
In this post, you’ll learn:
- Why predictive intelligence is mission-critical
- Practical frameworks and implementation strategy
- Real-world results from transformations
Whether you’re a CTO, founder, product manager, or engineering lead — you’ll walk away with a blueprint for implementing Predictive BI with confidence and measurable ROI.

Why Predictive BI Matters Now
As organizations scale, data grows exponentially — from IoT sensors and SaaS interactions to ERP and CRM workflows. Without predictive intelligence, businesses risk inefficiencies and lost opportunities.
What Happens Without Predictive BI?
- Overstocked inventory and lost sales due to poor forecasting
- Reactive operations, leading to downtime and inefficiencies
- Cybersecurity threats that go unnoticed until it’s too late
Where Predictive BI Is Making an Impact
- Healthcare: Predict patient admissions to reduce staffing gaps
- Logistics: Optimize routes to reduce fuel consumption by 15%
- SaaS: Improve conversion rates by 20% using behavioral analytics
- Manufacturing: Detect maintenance needs before equipment fails
The Cost of Doing Nothing
Legacy BI systems create:
- Data silos
- Manual reporting delays
- High operational costs
Modern enterprises need a scalable, integrated Predictive BI ecosystem — guided by experts who understand both technology and industry context.
Predictive BI Framework & Best Practices
Implementing Predictive BI is not a one-time task — it’s a structured journey. Below is the recommended implementation roadmap.
1. Define Clear Business Objectives
Align predictive goals to measurable KPIs such as churn reduction, seasonal demand forecasting, or supply chain efficiency.
2. Conduct Data Inventory & Quality Assessment
Audit data sources (ERP, CRM, IoT sensors, finance systems) and evaluate them based on:
- Completeness
- Accuracy
- Timeliness
High-quality input = reliable predictions.
3. Choose Scalable Architecture
Adopt Lambda or Kappa architecture to support:
- Real-time analytics
- Batch processing
- Cost efficiency
4. Select the Right Tech Stack

5. Iterative Model Development
Use Agile sprints, A/B testing, and continuous retraining to maintain accuracy as data evolves.
6. Embed Security & Compliance
Implement:
- Encryption
- RBAC
- Audit logs
- SOC 2/HIPAA compliance
7. Monitor, Optimize & Operationalize
Deploy model drift alerts and automated dashboards.
Quick Wins:
- Add anomaly alerts for trend deviations
- Enable self-service access for end users
8. Build a Data-Driven Culture
Train teams, provide documentation, and make insights accessible.
Do’s & Don’ts of Predictive BI
Do: Invest in data governance early
Don’t: Overcomplicate early models
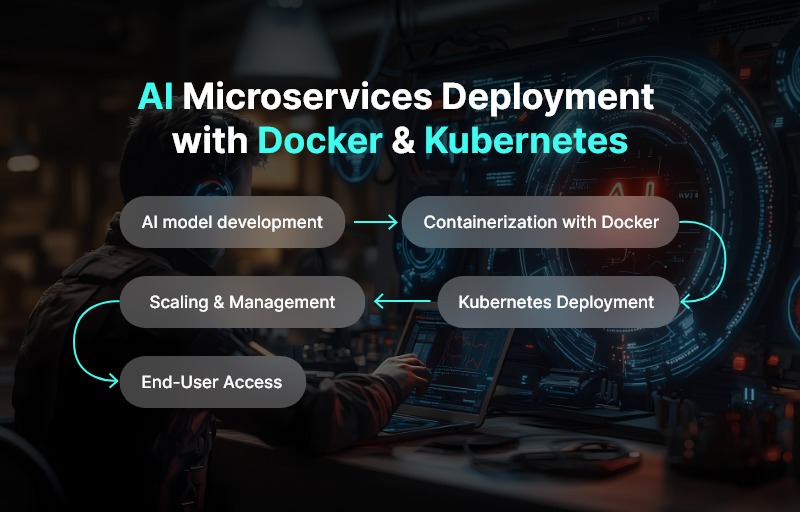
Do: Containerize deployments (Kubernetes, Docker)
Don’t: Ignore model explainability — stakeholder trust matters
How Andolasoft Accelerates Predictive BI Adoption
Andolasoft offers end-to-end expertise:
- Custom Web & Mobile Engineering: Predictive dashboards and apps
- SaaS Product Engineering: Scalable multi-tenant architecture
- BI, AI & ML Solutions: End-to-end model pipelines
- Application Modernization: Migration to cloud-native stacks
- Cloud, DevOps & Automation: Predictive CI/CD and automated retraining
With Andolasoft as a technology partner, organizations avoid:
- Data silos
- Costly architectural missteps
- Underutilized analytics investments
Customer Success Example
- Challenge: Predict patient admission volumes to reduce ER wait times.
- Solution: Real-time forecasting deployed with cloud-native predictive framework.
Results in 6 Months:
- 40% reduction in ER wait times
- 25% improvement in staffing efficiency
- 30% infrastructure savings through modernization
MedSecure now scales confidently with predictive capabilities embedded across operations.
Key Takeaways
- Predictive BI converts raw data into forward-looking insights that drive measurable business impact.
- High-quality data, scalable architecture, and governance are foundational.
- Continuous model training and DevOps practices ensure accurate forecasting.
- Security, compliance, and explainability must be included from day one.
- Working with Andolasoft accelerates deployment and avoids implementation pitfalls.