Introduction:
MemcacheD is easy yet powerful. It’s manageable design promotes fast deployment, ease of exaggeration, and solves many problems related to large data caches. It has its inbuilt APIs which provide a very large hash table distributed across multiple machines & uses internal memory management which is more efficient in the simplest use cases because it consumes comparatively less memory for metadata. MemcacheD supports only String data type which are ideal for storing read-only data.
Memcached is a volatile in-memory key-value origin. It is rude, multi-threaded and used primarily for caching objects.
Redis is an open source in-memory data structure store which also can be used as a database as well as caching. It supports almost all types of data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes through radius queries. Redis also can be used for messaging system used as pub/sub.
Internal Architecture:
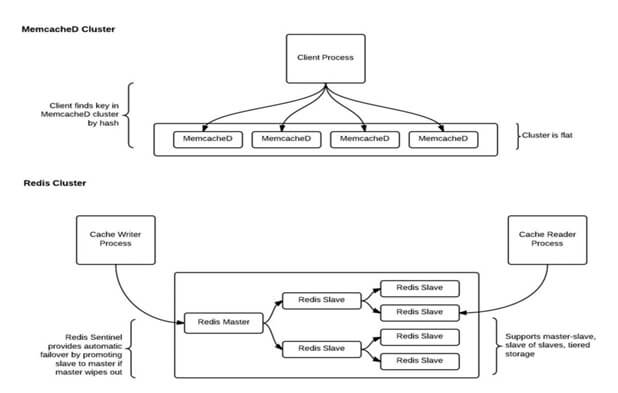
Here are the key points to consider,
Installation:
Installing Redis is so much easier. No dependencies required.
Memory Usage:
MemcacheD’s internal memory supervision, while not exactly a substitute to Redis; Is more efficient because it consumes comparatively less memory resources for metadata. For easy key-value pairs, MemcacheD is more memory efficient than Redis. Redis is more memory efficient, only after you use Redis hashes.
Persistence:
If you are using MemcacheD, data might be lost with a restart and rebuilding cache is a costly process. On the other hand, Redis can handle persistent data. By default it syncs data to the disk at least every 2 seconds, offering optional & tuneable data persistence meant to bootstrap the cache after a planned shutdown or an unintentional failure. While we tend to regard the data in caches as volatile and transient, persisting data to disk can be quite valuable in caching scenarios.
Replication:
MemcacheD does not support replication, whereas Redis supports master-slave replication. It allows slave Redis servers to be the exact copies of master servers. Data from any Redis server can replicate to any number of slaves. Replication can be used for implementing a cache setup that can withstand failures and find the maintenance for uninterrupted facilitation to the application.
Storage type:
MemcacheD stores variables in its memory & retrieves any information directly from the server memory instead of hitting the database again. On the other hand, Redis is like a database that resides in memory. It executes (reads and writes) a key/value pair from its database to return the result set. Developers use Redis for real-time metrics & analytics too.
Read/Write Speed:
MemcacheD is very good to handle high traffic websites. It can read lots of information at a time and give you back at a great response time. Redis can neither handle high traffic on read nor heavy writes.
Data Structure:
MemcacheD uses strings and integers in its data structure. Hence, everything you save can either be one or the other. With integers, the only data manipulation you can do is adding or subtracting them. If you need to save arrays or objects, you will have to serialize them first and then save them. To read them back, you will need to un-serialize.
In comparison Redis has stronger data structures, which can handle not only strings & integers but also binary-safe strings, lists of binary-safe strings, sets of binary-safe strings and sorted sets.
Key Length:
MemcacheD’s key length has a maximum of 250 bytes, whereas Redis has a maximum of 2GB.
Here is the benchmarking result by DB-Engines, which clearly shows the leader.
Conclusion:
Use Redis, if you need to do operations on cached datasets at once or need to spread one enormous cache over a geographically challenged area. Read-write splitting against caching will enormously help performance and alleviate the cache connection starvation.
On the other hand, you might want to stick to Memcached for its simplicity, reliability and speed.
SEE ALSO: How to Install and Configure Redis Server on Centos/Fedora Server
If you’re thinking anything on Ruby on Rails, get in touch with Andolasoft’s experts. Let’s convert your idea into an App.
Have something to add to this topic? Share it in the comments.