Not so long, just ten years ago, the Rails framework was written in Ruby programming language.
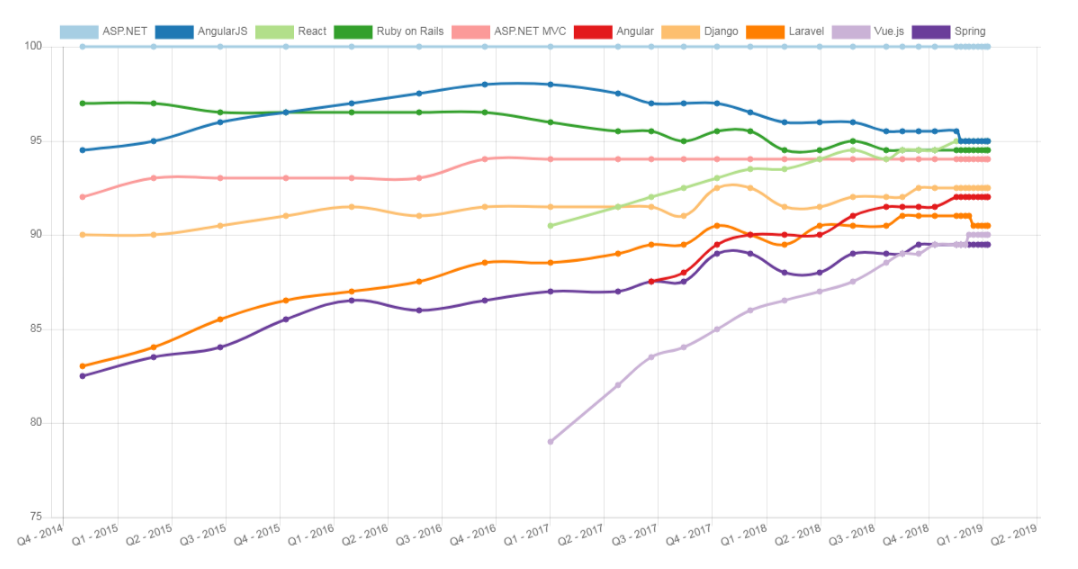
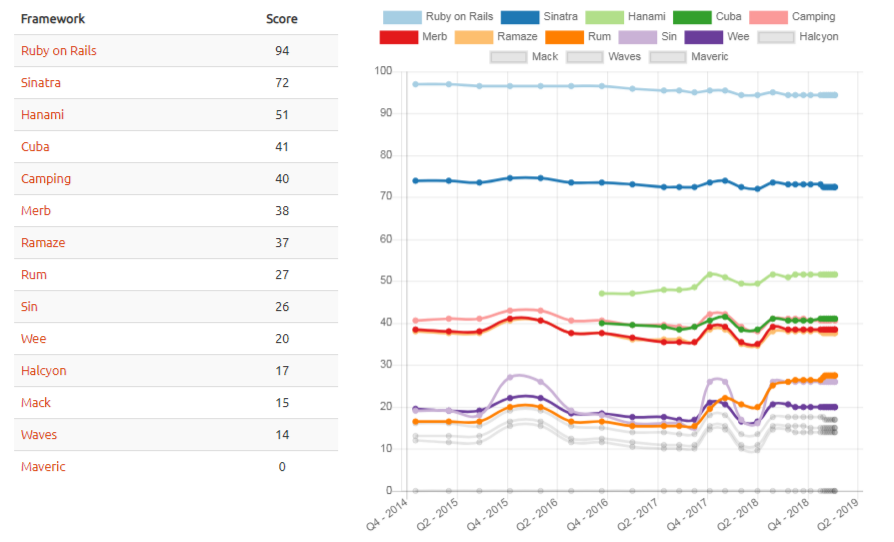
According to Hotframework ranking statistics, “Rails reside in the 4th place at the overall catalog of frameworks used now-a-days”.
 Source: Hotframeworks.com
Source: Hotframeworks.com
GitHub warehouse, StackOverflow query and questions, and Google Trends all are displaying the same statistics.
Overall Framework Catalog Ranking
 Source: Hotframeworks.com
Source: Hotframeworks.com
So, the first question arises, why this Ruby on Rails is so popular between both developers and entrepreneurs?
Many merchandise owners think Ruby web development is the most prolific way to build web applications. Well, it’s not an uncovered claim. It permits efficient ways for structuring applications at every step of the development procedure when many significant mechanisms can be generated as an alternative to being coded.
Never miss an update for us. Join 10,000+ marketers and leaders.
Ruby on Rails includes many established techniques and methods, familiar by both beginners and experienced developers, to deliver high-quality software. So, it would be easier to maintain the code in the future even, the addition of new features and making other changes would be like a piece of cake also.
First let’s see, how it works?
Well, Ruby development works for countless projects; however, it is an ideal option if your site or app refers to one of the mentioned classes:
- E-commerce: Ruby on Rails offers significant forms with very familiar user-friendly feature and modular based approach for most e-commerce sites.
- Content Management: Ruby web development would be the perfect choice for those websites which exhibit lots of database-friendly content such as the article, audio, video etc. It gives the easiest navigation to the site, upload and manages content as well.
- Custom Database Solutions: ROR works perfectly at higher database configuration for different business models.
- Membership Sites: Rails is good for subscription sites, membership site and social networking enabled sites. It has a number of plug-ins, which helps resolve approximately any job of social networking.
Sites like Shopify, Hulu, Groupon, Twitter, ZenDesk, YellowPages, and GitHub has developed with Ruby on Rails.
Here at Andolasoft, we also have vast experience in building projects on Ruby on Rails. Below are only a few examples:
Now come to the main query, Why Ruby on Rails is so popular?
Ruby on Rails’ reputation between developers and business owners has risen rapidly. Let’s find out some reasons.
1. Ruby is an ideal answer for MVP development
Development of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to authenticate the thought with a user base is the baseline for a startup approach. Startups’ software development procedure is often limited by time and budget. So, it is essential to find the development team who would run programming tools. Below I have tried to explain a few reasons why it is good for building an MVP.
- Fast programming: The tempo of MVP development in Ruby is much advanced in contrast with that incomparable language such as PHP or Python. When you’re into startup you always need to manufacture products as fast as possible. Ruby with its built-in development tools and handy elements allows you to speed up the development procedure and focus on your core business.
- Strong Ecosystem and Higher Compatibility. Ruby on Rails having an enormous set of features such as multi-platform compatibility, object-oriented, bunch of free plugins (gems) and best compatibility with other frameworks.
- Save on development costs: Rails’ machinery significantly clips the financial plan of the project, which is particularly precious for startups. Also, RoR does not involve any costs if you want to re-use, change, duplicate and allocate it.
- Easy to scale: Startups get hold of a working model inside a short time without spending much funds. This model may develop into a complete application with fewer efforts.
2. Easy API Formation for Mobile Apps
Application developed with Ruby on Rails uses RESTful structural design by default. It allows APIs creation easier and it is a well-recognized model among mobile and web programmers as well. You do not require hiring a new developer to implement RESTful code either.
3. Ruby is perfect for agile projects
RoR’s modular design helps to reproduce the instant changes rapidly with no loss in code and quality. Product proprietor is also able to give immediate feedback, and new versions can be implemented instantly. Automated tests in Rails structure help make sure the lack of bugs throughout code adjustment and it does not require extra documentation.
4. Community support
Community support for Ruby on Rails is just amazing – Ruby developers can get free online tutorials. The Ruby developer community forever keeps the framework advanced.
5. Automation and Development Smoothness
This is part where developers love Ruby on Rails. The framework automates many manual odds so that developers can put their focus on the project’s core features. It makes sure the immense efficiency of development procedure where the product proprietors get impressed.
I’ve worked with the team at AndolaSoft on multiple websites. They are professional, responsive, & easy to work with. I’ve had great experiences & would recommend their services to anyone.
Ruthie Miller, Sr. Mktg. Specialist
Salesforce, Houston, Texas

Last but not least, the framework offers economical, quick and dependable testing, which create it a charming spot for developers.
In other hands, outstanding maintain and automated structure of Ruby on Rails are the main reasons why it is so demand able.
Now that you know, what is Ruby on Rails used for and why it is popular for many developers and gainful for an extensive range of entrepreneurs. We could say it is one of our favorite development tools. In the end, Ruby on Rails outsources permits you to get a project within less period of time without giving up quality and performance of your application or website.