In the field of mobile app development, React Native stands as a beacon of cross-platform efficiency and developer-friendly app development.
It helps in building applications for multiple platforms with a single codebase and has propelled it to the forefront of the development world.
Yet, even in the midst of this brilliance, the reality remains crystal clear: React Native, though considered as one of the best frameworks, is not without its challenges.
Imagine a sophisticated toolkit that empowers developers to build stunning applications for both iOS and Android, harmonizing the art of coding with the poetry of seamless user experiences.
It’s time to dive into the nuanced world where excellence meets challenges, and developers emerge as skilled navigators steering their way to success in the realm of hybrid mobile app development.
In this blog, we’ll explore the common hurdles faced during React Native app development and unveil effective strategies to mitigate them, ensuring a smoother voyage for developers.
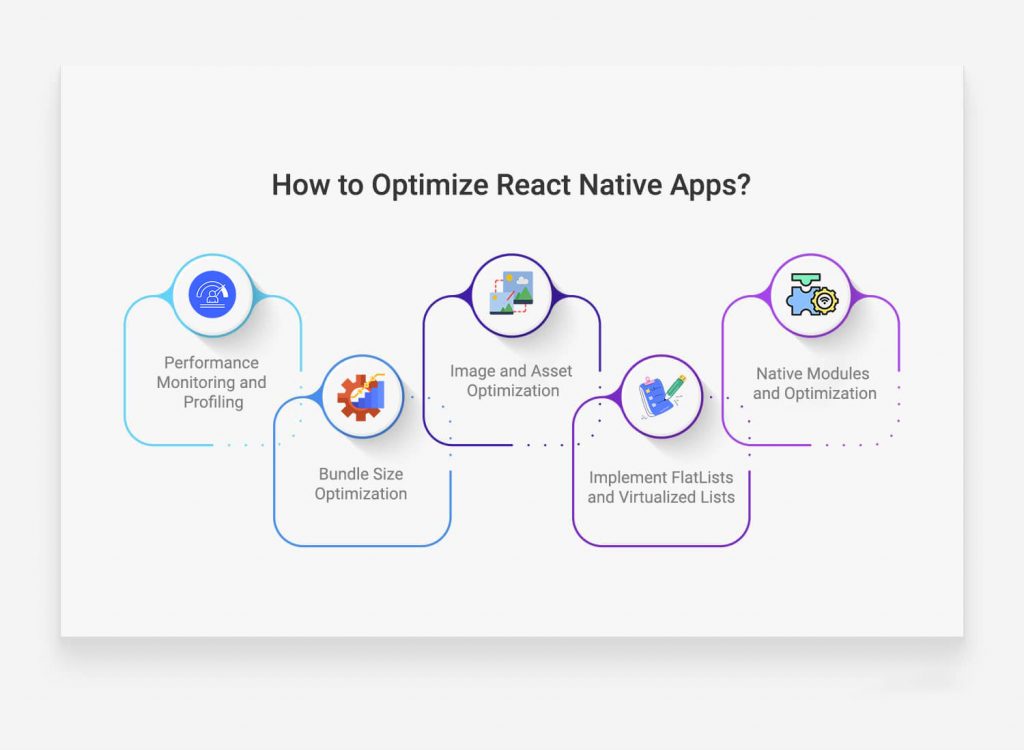
Performance Optimization:
- Challenge: Achieving optimal performance can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex applications.
- Mitigation Strategy: Implement performance monitoring tools, conduct regular profiling, and optimize code using techniques like code splitting and lazy loading to enhance app responsiveness.
Native Modules Integration:
- Challenge: Integrating native modules can be tricky, and developers may encounter compatibility issues.
- Mitigation Strategy: Thoroughly research and choose well-maintained libraries for native module integration. Stay updated with React Native releases and community contributions to ensure compatibility with the latest versions.
Limited Access to Native APIs:
- Challenge: React Native may not provide direct access to certain native APIs, necessitating workarounds.
- Mitigation Strategy: Explore third-party libraries or create custom native modules to bridge the gap. Keep a keen eye on updates from the React Native community, as new solutions and improvements are frequently introduced.
Learning Curve:
- Challenge: Developers transitioning from other frameworks or native app development may face a learning curve.
- Mitigation Strategy: Invest time in comprehensive training programs, online courses, and documentation. Encourage collaboration within development teams to share knowledge and experiences. Gradually introduce React Native in small projects to build proficiency.
Debugging and Troubleshooting:
- Challenge: Identifying and resolving issues can be challenging, particularly when debugging across multiple platforms.
- Mitigation Strategy: Leverage debugging tools provided by React Native and use platform-specific tools for deeper insights. Regularly check the official documentation and community forums for troubleshooting tips and solutions.
Version Compatibility Issues:
- Challenge: Keeping up with the rapidly evolving React Native ecosystem can lead to version compatibility issues.
- Mitigation Strategy: Establish a versioning strategy for your project, carefully evaluating the impact of upgrading. Monitor community discussions, and plan updates during periods of low development activity to minimize disruptions.
Security Concerns:
- Challenge: Security is a paramount concern, especially when integrating third-party modules or dealing with sensitive data.
- Mitigation Strategy: Regularly audit dependencies, adhere to secure coding practices, and stay informed about security updates in both React Native and related libraries. Implement encryption and other security measures to protect user data.
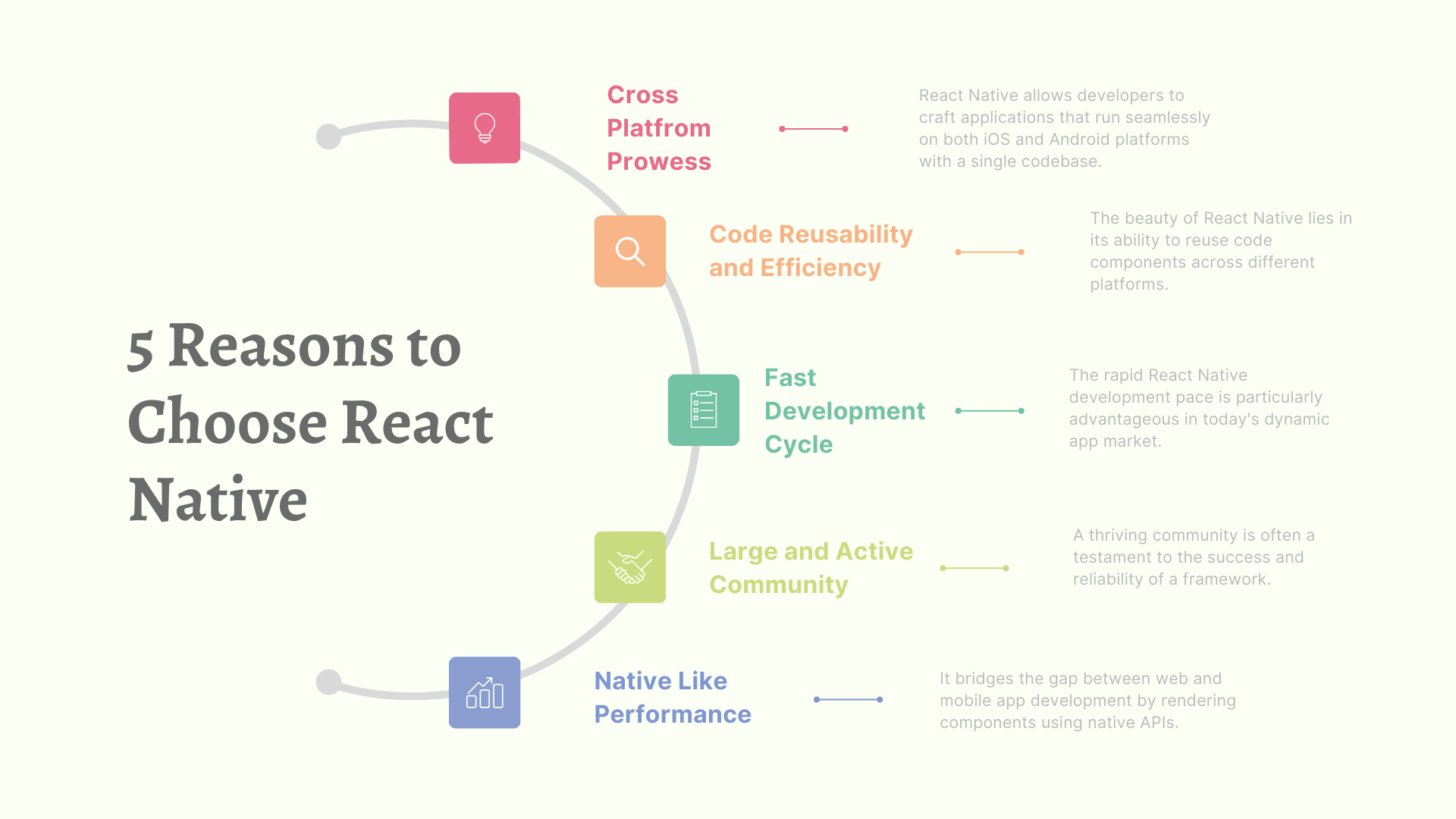
5 Reasons to Choose React Native For Mobile App Development?
1. Cross-Platform Prowess:
React Native allows developers to craft applications that run seamlessly on both iOS and Android platforms with a single codebase.
This cross-platform capability significantly reduces development time and costs, making it an attractive choice for businesses aiming to reach a wider audience.
2. Code Reusability and Efficiency:
The beauty of React Native lies in its ability to reuse code components across different platforms.
Developers can write code once and deploy it on multiple devices, eliminating the need to build separate codebases for iOS and Android.
This not only accelerates development but also ensures consistency and easier maintenance.
3. Fast Development Cycle:
It comes equipped with a “Hot Reloading” feature, enabling developers to instantly see the results of the latest code changes without restarting the application.
This accelerates the development cycle, allowing for quick iterations and efficient debugging.
The rapid React Native development pace is particularly advantageous in today’s dynamic app market.
4. Large and Active Community:
A thriving community is often a testament to the success and reliability of a framework.
It boasts a large and active community of developers who contribute to its growth.
This means access to a wealth of resources, third-party libraries, and solutions to common challenges.
The community support ensures that developers are not alone in their journey with React Native.
5. Native-Like Performance:
It bridges the gap between web and mobile app development by rendering components using native APIs.
This results in a native-like performance, ensuring that the apps not only look but also feel like native applications.
Users get a smooth and responsive experience, while developers benefit from the efficiency of a single codebase.
Top 6 Mistakes to Avoid During React Native App Development
1. Ignoring Platform Differences:
It is celebrated for its cross-platform capabilities, but that doesn’t mean developers can ignore platform nuances.
Neglecting the differences between iOS and Android can lead to unexpected issues.
Always be aware of platform-specific guidelines and ensure your code adapts gracefully to each environment.
2. Overlooking Performance Optimization:
Performance is key in the world of mobile apps. Failing to optimize your React Native application can result in sluggish performance and frustrated users.
Keep an eye on memory usage, utilize performance monitoring tools, and implement best practices to ensure your app runs smoothly across various devices.
3. Not Testing on Real Devices:
While emulators are handy during development, relying solely on them can be a mistake.
Real devices may behave differently, and testing on a variety of actual devices is crucial to catch platform-specific issues, screen size variations, and performance disparities that might be overlooked in emulation.
4. Ignoring Component Lifecycle Methods:
It provides a set of lifecycle methods that are vital for managing component state and handling updates.
Neglecting to understand and leverage these methods properly can lead to memory leaks, unnecessary re-renders, and other performance bottlenecks.
Familiarize yourself with component lifecycles and use them judiciously.
5. Dependency Overload:
Third-party libraries can be a lifesaver, but an excess of dependencies can quickly turn into a nightmare.
It’s essential to evaluate the necessity and reliability of each library before integrating it into your project.
Too many dependencies can bloat your app, increase the likelihood of conflicts, and hinder maintainability.
6. Lack of Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD):
Failing to implement a robust CI/CD pipeline is a common mistake in React Native development.
Continuous integration and deployment practices help catch errors early, ensure code consistency, and streamline the release process.
Set up automated testing and deployment pipelines to enhance the reliability and efficiency of your development workflow.
Conclusion:
React Native’s challenges are not insurmountable, and with the right strategies, developers can navigate through them effectively.
By staying informed, embracing best practices, and actively participating in the community, developers can ensure a successful and secure app development journey.
As the framework evolves, these mitigation strategies will continue to play a crucial role in fostering a robust and efficient React Native development environment.