With the increasing number of apps going live on the web, it’s becoming common to see that they use multiple servers. This is mainly due to scalability and availability purposes. But, these types of applications are also often not as responsive as they should be. Using a simple gem called DynamoDB and Memcached will allow you to achieve higher performance in your Rails app. Let me explain,
What is Memcached
Memcached is a high performance, free and open source distributed memory caching system used to speeding up dynamic web applications by alleviating database load. Memcached is simple yet powerful. Its simple design promotes quick deployment, ease of development, and solves many problems facing large data caches.
It is used for speeding up dynamic web applications by reducing database load. In other words, every time a database request is made it adds additional load to the server. Memcached reduces that load by storing data objects in dynamic memory (think of it as short-term memory for applications). Memcached stores data based on key-values for small arbitrary strings.
How does Memcached work?
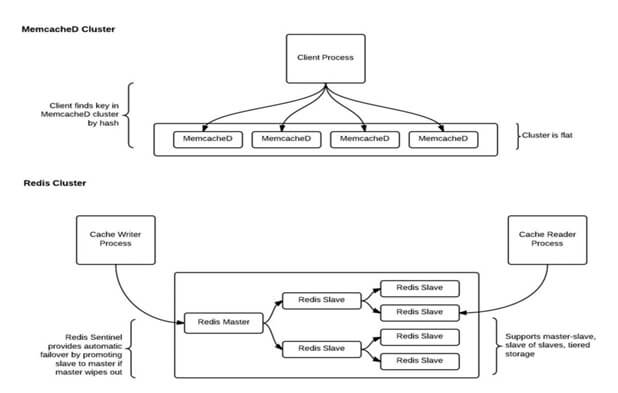
Memcached is comprised of four main components
- Client software – Which is given a list of available Memcached servers
- A client-based hashing algorithm – Chooses a server based on the “key”
- Server software – Stores values and their keys into an internal hash table
- LRU – Determines when to throw out old data or reuse memory
Each item is comprised of a key, expiration time, and raw data.
At a high-level Memcached works as follows:
- The client requests a piece of data which Memcached checks to see if it is stored in cache.
- There are two possible outcomes here:
- If the data is stored in cache: return the data from Memcached (no need to check the database).
- If the data isn’t stored in cache: query the database, retrieve the data, and subsequently store it in Memcached.
- Whenever information is changed or the expiry value of an item has expired, Memcached updates its cache to ensure fresh content is delivered to the client.
A few important points about Memcached architecture include:
- Data is only sent to one server.
- Servers don’t share data.
- Servers keep values in RAM. If RAM runs out the oldest value is discarded.
What is DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability. With DynamoDB, you can create database tables that can store and retrieve any amount of data and serve any level of request traffic. You can scale up or scale down your tables’ throughput capacity without downtime or performance degradation.
DynamoDB is a particularly good fit for the following use cases
- Applications with large amounts of data and strict latency requirements
- Server less applications using AWS Lambda
- Data sets with simple, known access patterns
Installing Memcached
There are a few ways you can install Memcached. Depending on which system you’re using, the method will vary. As outlined on the official Memcached Installation Wiki, installation from a package is simple.
Using Memcached with DynamoDB in Rails
Memcached is a quick in-memory protest reserving framework that can make Rails run much quicker with not very many changes. Memcached will work on any database used in Rails application.
When the table is small and request volume is low this isn’t much of an issue, but as your database and user volume grow, these can impact the performance of your application. In such cases Memcached plays an important role to reduce the database load by caching the request object in memory.
To use Memcached in Rails app, follow the below steps
Install dalli gem
[code language=”css”]gem ‘dalli'[/code]
Add “dalli” gem to your gem file and install it.
Development/Production file
[code language=”css”]config.cache_store = :dalli_store</em><em> </em><em>config.action_controller.perform_caching = true[/code]
Add the above lines in your development.rb or production.rb file as per the requirement
Add Memcached in your method
[code language=”css”]search_query = "user_id = :user_id AND is_approved = :is_approved"
search_param = {":user_id" => params[:user_id], ":is_approved" => ‘t’}
all_games = Rails.cache.fetch(‘all_lists’, expires_in: 2.minutes)
{
do_scan(Article.table_name,search_query,search_param)
}[/code]
The above query syntax is an example of combination of Memcached and DynamoDB. In this example once the query executed and the result will store in the “all_list” key of the Memcached and expire after 2 minutes automatically.
Conclusion:
DynamoDB and Memcached is a powerful combination for your Rails app. If you’re looking to improve the performance of your Rails application, this may be the solution for you.
DynamoDB and Memcached involves storing information in an external database, which can be retrieved with a single call. This will allow you to avoid the constant querying of data from your application’s memory.
There are many benefits to this gem, but most importantly, increased response time for your application. Faster response times mean less downtime and more satisfied customers.
You have rails application but don’t know how to maximize the performance with DynamoDB and Memcached. Andolasoft has experienced rails developer who has good hands on DynamoDB and Memcached. So fell free to discuss about your project. Book a free consultation